the most frequent bacteria is staphylococcus aureus
cartilage damage can occur by 8 hours
most commonly affected joints in descending order
knee (~ 50% of cases) >
hip >
shoulder >
elbow >
ankle >
sternoclavicular joint
found in IV drug users
pseudomonas aeruginosa was most common pathogen in 1980's
staphylococcus aureus is now the most common pathogen in all patients, including IV drug users
risk factors
age > 80 years
medical conditions
diabetes
rheumatoid arthritis
cirrhosis
HIV
history of crystal arthropathy
endocarditis or recent bacteremia
IV drug user
recent joint surgery
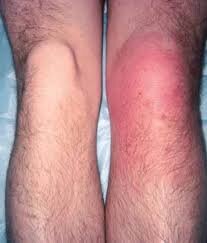
Symptoms
pain in affected joint
fevers (only present in 60% of cases)
may appear toxic
Inability to bear weight
inability to tolerate PROM
3 etiologies of bacterial seeding of joint
bacteremia
direct inoculation from trauma or surgery
contiguous spread from adjacent osteomyelitis
Blood test :
WBC >10000
ESR >30
CRP > 5
Characteristic findings
joint fluid appears cloudy or purulent
cell count with WBC > 50,000 is considered diagnostic for septic arthritis, however lower counts may still indicate infection
prosthetic joint with WBC >1,100 is considered septic
gram stains only identifies infective organism 1/3 of time
glucose less than 60% of serum leve
Joint fluid aspirate
gold standard for treatment and allows directed antibiotic treatment
should be analyzed for
cell count with differential
gram stain
culture
glucose level
crystal analysis
septic arthritis occurs concurrently with gout or pseudogout in < 5% of cases
Differential diagnosis
Crystal arthropathy
gout
pseudogout
Cellulitis
Bursitis
treatment: ATB + lavage